For a detailed visual experience, access the images within the App to conserve up to 80% of your data. NASA's remarkable detection of an extensive water vapor cloud encircling a far-off quasar has revolutionized our insights into the early cosmos and sparked inquiries into the omnipresence of water in the universe's fabric. Unveiling the Cosmic Water Realm The gargantuan water reservoir, first detected in 2011, is encircling a quasar identified as APM 08279+5255. This astronomical object harks back to a time when the universe was merely 1.6 billion years old, offering a rare glimpse into the nascent cosmos. The staggering amount of water in this ancient system challenges our preconceptions about the elemental composition of the early universe. Quasars, the most luminous entities in the universe, are fueled by supermassive black holes. The central black hole of APM 08279+5255 is colossal, with a mass 20 billion times that of our Sun. This cosmic juggernaut emits energy equivalent to a million billion suns, resulting in an environment where water vapor extends for hundreds of light-years. This pivotal water reservoir discovery is in line with recent breakthroughs in our understanding of cosmic phenomena. For instance, a subtle variation in light recently revealed the origin of an enigmatic deep-space event, highlighting how minor observations can lead to substantial astrophysical discoveries. Matt Bradford, a scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, remarks on the distinctiveness of this setting in a study featured in the Astrophysical Journal Letters: “The environment around this quasar is genuinely unparalleled in its capacity to generate such an immense quantity of water.” This revelation underscores the universal presence of water, even in the most ancient eras. Characteristics of the Interstellar Oasis The water vapor encircling APM 08279+5255 displays extraordinary properties that distinguish it from standard galactic conditions. These exceptional traits arise from the powerful infrared and X-ray emissions of the quasar. Here is a summary of its extraordinary features: Temperature: Approximately -63°C, which is significantly warmer than average galactic conditions Density: 10 to 100 times greater than similar cosmic settings Extent: Spans hundreds of light-years around the quasar The conditions of this cosmic aqueous domain are starkly different from those in our local galaxy. The intense environment crafted by the quasar's radiation fosters the condensation of water to an extraordinary extent, presenting a unique arena for examining the properties of matter under extreme conditions. While this discovery is of monumental importance, it's also crucial to acknowledge that advancements in space exploration are expanding horizons in various domains. For example, China recently introduced a hypersonic aircraft capable of circumnavigating
Recent
See All
2025-05-04
A Discovery of Hundreds of Dinosaur Footprints Dating Back 166 Million Years Has Been Made in England
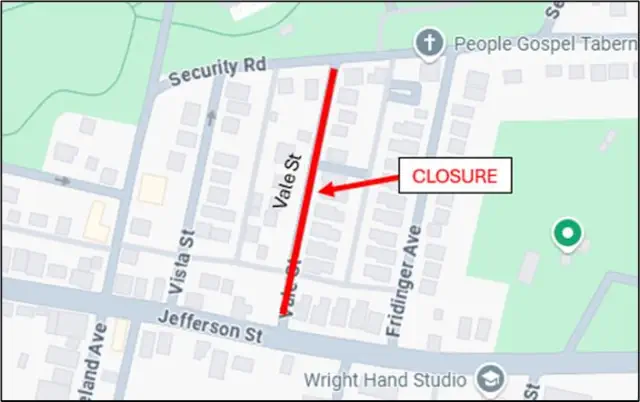
2025-05-04
Traffic Notice: Vale Street (January 9 & 13)

2025-05-04
Consensus Guidelines for Histological and Clinical Reporting in HS

2025-05-04
What are the reasons for adding fluoride to drinking water? Experts share their insights.

2025-05-04
Abbott names Anwar and Salsman to the Texas Low-Level Radioactive Waste Disposal Compact Commission.

2025-05-04
Breton, a massive great white shark weighing 1,400 pounds, has made his way back to the shores of Florida.

2025-05-04
Pluto might have acquired its largest moon following a primordial waltz and embrace.

2025-05-04
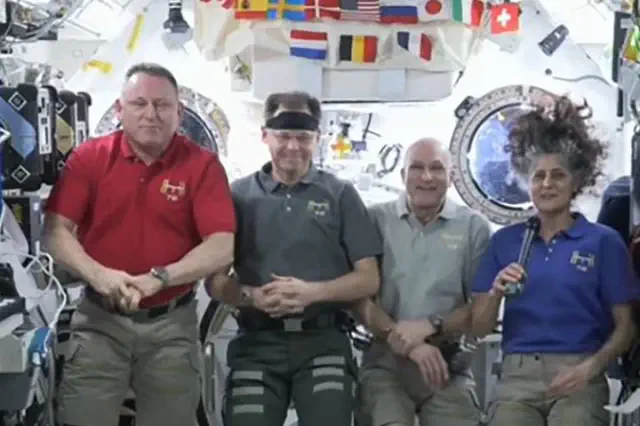
NASA astronauts who have been stuck in space for several months have provided an update on their current situation.

2025-05-04
ISRO's SPADEX docking mission has been delayed for the second time, but all satellites remain secure.

2025-05-04
Private Employment Slows Down in the United States
Newsletter
Get life tips delivered directly to your inbox!
